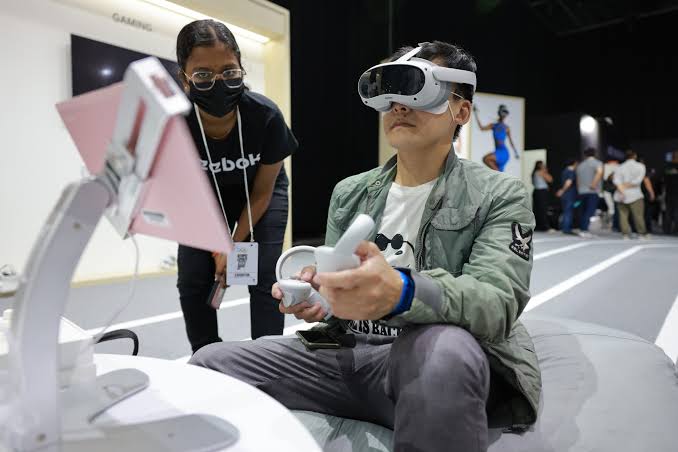
Virtual reality (VR) has evolved significantly from its early days as a niche gaming technology. By July 2025, VR headsets are no longer just entertainment devices but have grown into powerful tools used across various industries.
The market has expanded with the introduction of lighter, wireless, high-resolution headsets. Devices like Meta Quest 4, Apple Vision Pro 2, and Sony PlayStation VR3 now offer immersive experiences with lifelike graphics, enhanced motion tracking, and better user comfort.
While gaming remains the most recognized application, the possibilities of VR now stretch into education, healthcare, retail, real estate, and even remote work, promising a future where immersive digital environments will be integrated into everyday life.
Advancements in VR Hardware and Design
The latest generation of VR headsets focuses on user comfort, clearer visuals, and seamless interaction. Devices launched in 2025 have improved field of view, higher refresh rates, and better optical clarity.
Manufacturers have reduced headset weight by integrating lightweight materials and energy-efficient processors. Many new models offer inside-out tracking, eliminating the need for external sensors and allowing greater mobility.
Additionally, wireless connectivity through 6G and ultra-low-latency Wi-Fi has allowed users to stream VR content with minimal lag. Built-in AI chips now adjust visuals in real time based on the user’s gaze and position, creating a more personalized experience.
VR Gaming: A New Era of Immersion
Gaming continues to lead VR innovation. In 2025, the line between traditional gaming and virtual experiences is increasingly blurred. Major game developers have created exclusive VR titles that offer deep, story-driven narratives and multiplayer interactivity.
Games now include realistic haptics that simulate touch, allowing players to feel textures or pressure during gameplay. Full-body tracking suits, though still costly, are being adopted by competitive gamers and VR arcades for enhanced realism.
Social gaming spaces have also taken off. Platforms like VRChat and Rec Room now host millions of users daily, combining gaming with virtual social interaction, creating digital playgrounds where people build, play, and explore together.
Education and Virtual Learning Environments
The use of VR in education has grown rapidly. Schools and universities in Canada and globally now deploy VR headsets to create interactive, immersive lessons. Students can explore ancient civilizations, dissect virtual frogs, or simulate chemistry experiments without leaving the classroom.
In 2025, virtual campuses allow learners to attend lectures, collaborate with classmates, and engage in group projects in digital 3D environments. These spaces are particularly helpful for remote and international students seeking more engaging learning formats.
Medical schools use VR headsets to simulate surgeries and anatomy labs, offering a risk-free, hands-on learning experience that enhances knowledge retention and skill development.
Healthcare Applications and Therapy
Healthcare is another sector embracing VR beyond gaming. Therapists use VR headsets to treat patients suffering from PTSD, anxiety disorders, and phobias by placing them in controlled, therapeutic virtual environments.
In hospitals, VR is being used for pain distraction, especially in pediatric wards and burn units. Patients wear headsets during painful procedures and are transported to calming virtual landscapes to ease discomfort.
Physical rehabilitation programs in 2025 also benefit from VR. Patients recovering from strokes or injuries can perform guided exercises in virtual environments that encourage mobility and cognitive engagement under remote supervision.
Workplace Training and Remote Collaboration
VR has found its way into corporate training, especially in industries like aviation, manufacturing, and emergency services. Trainees now engage in realistic simulations that prepare them for high-risk scenarios without real-world danger.
In 2025, large organizations are using VR for onboarding new employees, offering virtual office tours, and teaching job-specific tasks through immersive simulations. This method is cost-effective and ensures consistency in training across multiple locations.
Remote collaboration is also evolving. VR headsets enable virtual meetings where participants interact with 3D avatars, share digital whiteboards, and manipulate virtual objects. This creates a more engaging alternative to traditional video conferencing.
Retail and Virtual Shopping Experiences
Retailers are using VR to revolutionize the shopping experience. Customers can now enter virtual stores, try on outfits using realistic avatars, and examine products from all angles before making a purchase.
In 2025, furniture and home decor companies are integrating VR with AR, allowing customers to virtually place furniture in their real homes to see how items would look and fit before buying.
The integration of blockchain for virtual goods is growing too. Some VR stores allow users to purchase NFTs or digital accessories for their avatars, blending e-commerce with virtual identity and gaming culture.
Real Estate, Tourism, and Architecture
The real estate industry is increasingly dependent on VR for virtual property tours. Potential buyers or renters can explore apartments, homes, or commercial buildings in full 3D detail without physically visiting them.
Tourism companies are offering virtual travel experiences where users can visit historical landmarks or exotic locations using VR. While not a replacement for physical travel, it helps people preview destinations or explore areas they might not afford to visit otherwise.
Architects and designers use VR to showcase 3D building models to clients. This allows stakeholders to walk through projects during the design phase, improving understanding and decision-making.
Challenges Facing the VR Industry
Despite the exciting potential, the VR industry still faces several hurdles. High-end headsets remain expensive, making them inaccessible for many users. Battery life, motion sickness, and hardware compatibility issues persist.
Privacy concerns are also rising. VR devices collect detailed data, including eye movement, gestures, and biometric feedback, raising questions about user consent and data protection.
In 2025, developers are under pressure to create more inclusive content, as not all VR environments are accessible to people with disabilities. There is also a growing need for ethical standards in the use of VR for psychological therapies and social platforms.
The Road Ahead for VR
Looking forward, the VR headset market is expected to become even more competitive and user-friendly. Integration with artificial intelligence, real-world sensors, and cloud gaming will continue to enhance performance and reduce costs.
As industries discover new applications, VR will expand far beyond gaming, influencing how people work, learn, heal, and connect. Developers are focusing on creating content that balances entertainment, functionality, and well-being.
The future of virtual reality headsets in 2025 is not just immersive—it’s transformative. With continued innovation and thoughtful implementation, VR has the potential to reshape everyday experiences, making virtual engagement a seamless part of modern life.