As of July 2025, biometric authentication has become a core component of digital security systems worldwide. From unlocking smartphones to securing sensitive financial transactions and enabling seamless airport check-ins, biometric technologies are increasingly relied upon for their ability to uniquely and accurately verify individual identities. As cyber threats grow more sophisticated, biometric authentication offers a powerful solution that blends convenience, efficiency, and robust protection.
This modern approach to identity verification leverages physical or behavioral characteristics—such as fingerprints, facial structure, voice patterns, or even the way a person types or walks—to create secure and personalized access protocols.
What Is Biometric Authentication?
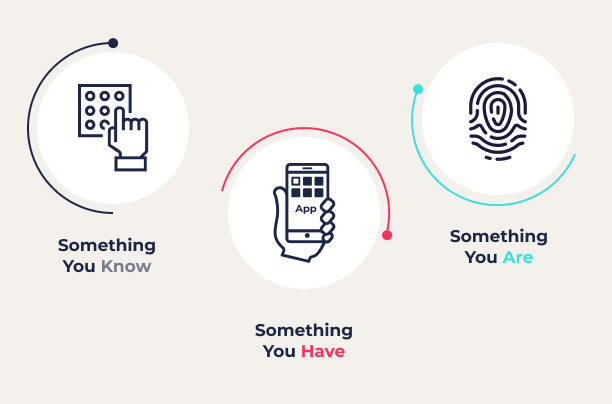
Biometric authentication is a method of verifying a person’s identity based on unique physiological or behavioral traits. The most common biometric systems include:
- Fingerprint recognition
- Facial recognition
- Iris or retina scanning
- Voice recognition
- Palm vein and hand geometry
- Behavioral biometrics (like keystroke dynamics or gait)
These identifiers are difficult to replicate, making biometrics a highly secure alternative to traditional passwords or PINs, which can be guessed, stolen, or forgotten.
Enhanced Security and Identity Protection
One of the most important benefits of biometric authentication is its superior security compared to conventional methods. Since biometric data is unique to each individual, it significantly reduces the risk of impersonation, fraud, and unauthorized access.
Key security advantages include:
- Harder to forge or steal: Unlike passwords or ID cards, biometric traits cannot be easily duplicated or shared.
- Two-factor and multi-modal security: Biometrics can be combined with passwords or tokens to create highly secure multi-factor authentication systems.
- Spoof detection technology: Modern systems are designed to detect attempts to fool them using photos, recordings, or fake fingerprints.
This level of protection is especially vital for banking apps, government services, and secure enterprise environments, where safeguarding user data is critical.
Improved User Convenience and Accessibility
Biometric authentication systems are not only secure—they’re also highly user-friendly. They eliminate the need to remember passwords, carry tokens, or go through time-consuming manual verification processes.
Here’s how they improve user experience:
- Faster access: Logging in via fingerprint or facial recognition takes seconds, improving workflow and productivity.
- Touchless interaction: In a post-pandemic world, facial and voice recognition offer hygienic, contactless authentication.
- Fewer password resets: Organizations can reduce IT support costs and employee downtime caused by forgotten credentials.
This seamless access is particularly valuable in high-volume settings like airports, hospitals, and office buildings where speed and simplicity are essential.
Cost-Effective in the Long Run
While the initial investment in biometric systems—hardware, software, and infrastructure—can be high, the long-term benefits often outweigh the costs. These systems reduce the need for physical ID production, access cards, and regular password maintenance.
Organizations benefit through:
- Lower administrative overhead: No need to manage or reset countless passwords.
- Reduced fraud-related losses: Enhanced security helps prevent costly breaches or identity theft.
- Scalability: Once a biometric system is in place, adding new users or locations is relatively simple.
As biometric technology continues to advance and become more affordable, even small and medium-sized businesses are adopting it to streamline operations.
Applications Across Multiple Sectors
The versatility of biometric authentication makes it suitable for a wide range of industries and use cases. Some of the most prominent include:
- Banking and Finance: Facial or fingerprint verification for mobile banking, ATM withdrawals, and customer onboarding.
- Healthcare: Securing electronic medical records and enabling fast, secure patient check-ins.
- Airports and Border Control: Facial recognition for immigration clearance, baggage handling, and boarding.
- Education: Student ID verification for exams and attendance tracking.
- E-commerce: Biometric login for online accounts and secure digital payments.
Each sector benefits from improved security, faster processes, and enhanced user confidence.
Stronger Compliance with Regulatory Standards
In response to growing concerns around data privacy and security, regulatory bodies around the world are tightening standards for identity verification. Biometric authentication systems, when properly implemented, can help organizations comply with requirements such as:
- GDPR (Europe)
- CCPA (California)
- NDPR (Nigeria Data Protection Regulation)
- FIDO2 and other global authentication standards
Biometric systems can offer audit trails, consent-based data usage, and encryption features that align with these evolving regulatory demands.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite their benefits, biometric systems come with important considerations:
- Privacy concerns: Biometric data is sensitive and irreversible. If compromised, it cannot be changed like a password. It must be stored and managed with high-grade encryption and security protocols.
- Bias and accuracy: Facial recognition systems have faced criticism over racial and gender bias. Continued improvements in AI training and diverse datasets are helping to address these issues.
- Consent and transparency: Users must be informed and give consent before their biometrics are collected or used. Organizations must prioritize ethical deployment.
In response to these concerns, more countries and companies are adopting clear biometric policies that ensure fairness, transparency, and responsible data handling.
Future Outlook: Where Biometric Authentication Is Headed
Looking forward, biometric authentication is poised to become even more integrated into our daily lives. Trends shaping the future include:
- Biometric wearables: Devices like smartwatches will authenticate users through pulse patterns, skin temperature, or movement signatures.
- Biometric blockchain solutions: Decentralized identity systems will use biometrics for secure verification without storing sensitive data centrally.
- Behavioral AI: Continuous authentication based on user behavior (typing speed, device handling) will silently verify identity in the background.
These innovations promise not only to enhance security but also to reduce friction, making digital life smoother and safer.
Final Thoughts
Biometric authentication is redefining what it means to be secure in the digital age. By combining cutting-edge technology with user-centric design, it offers a future where identity is both unique and verifiable, and access is both safe and simple. As more sectors adopt this method, and as ethical frameworks evolve to safeguard user data, biometrics will continue to shape the next generation of secure, intelligent systems. Businesses, institutions, and individuals alike stand to gain from embracing this powerful evolution in identity verification.



Really educating.
Security purpose
Fascinating