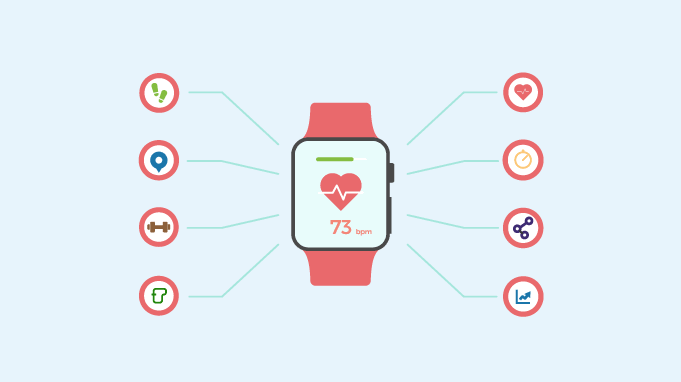
As of June 2025, smartwatches do much more than tell time or show notifications. They now have strong health features that monitor heart rate, sleep, blood oxygen, and stress. With AI chips, better sensors, and medical-level analysis, smartwatches help people manage their health better.
However, while these devices offer numerous health benefits, they are not without limitations. This article explores the current advantages and disadvantages of using smartwatches for health monitoring in 2025, helping users make informed decisions about incorporating wearable technology into their daily health routines.
Real-Time Tracking and Convenience
One of the standout benefits of smartwatches is their ability to provide real-time health tracking. Users can monitor heart rate, respiratory rate, steps taken, calories burned, and even hydration levels throughout the day. In 2025, brands like Apple, Samsung, Garmin, and Fitbit have fine-tuned their sensors to deliver more accurate and responsive data.
This real-time access is particularly useful during exercise, allowing users to adjust their pace or intensity for optimal performance. It also supports day-to-day wellness by offering visual insights into how lifestyle choices affect key health indicators. Unlike traditional medical equipment, smartwatches are non-invasive, lightweight, and always within reach—making them convenient companions for routine monitoring.
Early Detection of Health Issues
Advanced smartwatches in 2025 are capable of detecting abnormal patterns that may indicate potential health problems. For instance, prolonged irregular heartbeat alerts, consistently high blood pressure, or unusual sleep patterns can signal early signs of cardiovascular or metabolic conditions.
Some smartwatches are now FDA-cleared to perform ECG readings, track atrial fibrillation, and detect sleep apnea. These early warning systems have empowered many users to seek medical attention before symptoms escalate, potentially reducing the risk of serious complications. In this way, wearables serve as proactive tools that encourage preventive care rather than reactive treatment.
Personalized Health Insights
Through machine learning and cloud syncing, smartwatches now offer personalized health reports. These devices learn from a user’s habits over time and tailor recommendations to encourage healthier behaviors. For example, a smartwatch might suggest going to bed earlier after noticing poor sleep quality for several days or recommend a hydration break based on detected dehydration signs.
The addition of AI-driven coaching platforms in apps like Apple Health, Samsung Health, and Google Fit in 2025 means users can receive intelligent nudges throughout the day. These personalized insights help bridge the gap between raw data and actionable improvement, making it easier for users to build lasting wellness habits.
Motivation and Goal Setting
Smartwatches have transformed fitness and health tracking into a motivational experience. With daily goal reminders, achievement badges, streak rewards, and social sharing features, these devices gamify wellness, keeping users engaged and consistent.
The ability to track progress visually—like watching a fitness ring close or beating a weekly step goal—triggers a sense of accomplishment that motivates continued effort. For many users, this reinforcement has led to improved long-term adherence to fitness and diet routines. As of 2025, AI-enhanced challenge systems allow users to compete with friends or join virtual wellness communities, fostering accountability and motivation.
Seamless Integration with Healthcare Systems
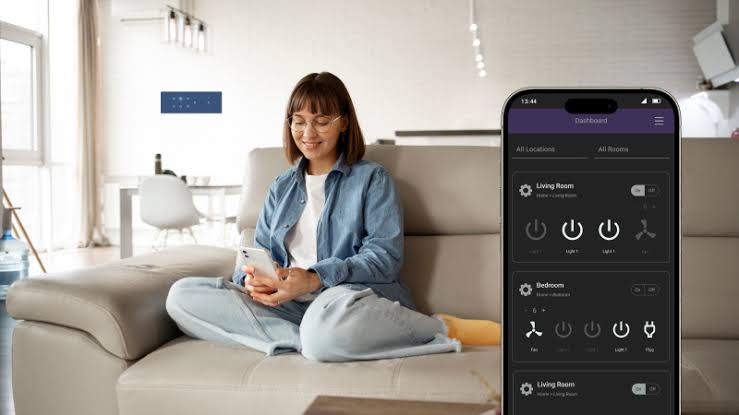
One of the newer advantages in 2025 is the growing ability of smartwatches to sync with healthcare providers. Devices can now integrate securely with electronic medical records (EMRs) via HIPAA-compliant platforms, allowing doctors to view patient-collected health data in real time or during telemedicine appointments.
This streamlining of information helps physicians offer more personalized care, track patient compliance with treatment plans, and make better-informed decisions. In some regions, smartwatch data is now accepted as part of routine health screenings or insurance wellness programs, reflecting their increasing medical credibility.
Battery Limitations and Data Accuracy
Despite technological improvements, smartwatches still face limitations. Battery life is a common issue, especially in devices packed with high-performance sensors and constant tracking features. Many users find themselves needing to recharge their smartwatch daily or every other day, which can interrupt overnight tracking or long-term data collection.
Moreover, while sensor accuracy has improved, it is not yet perfect. Factors such as skin tone, tattoos, ambient temperature, and device positioning can affect readings. This means that data from smartwatches should still be interpreted with caution, particularly when used as a standalone diagnostic tool.
Risk of Over-Reliance and Health Anxiety
As smartwatches grow more capable, users may develop a false sense of security or become overly dependent on them for health monitoring. In some cases, frequent alerts and health reminders can create unnecessary stress or health anxiety. Users may misinterpret benign symptoms or obsess over minor data fluctuations, leading to needless doctor visits or self-diagnosis.
This hyper-awareness can be counterproductive, especially for individuals with anxiety-related conditions. Experts in 2025 recommend that smartwatch users maintain perspective and consult healthcare professionals before making health decisions based solely on wearable data.
Privacy and Data Security Concerns
The growing use of health wearables also raises significant questions about data privacy. As smartwatches collect and transmit sensitive biometric information, concerns have been raised about who owns this data and how securely it is stored. In 2025, tech companies have made strides in encryption and transparency, but incidents of data breaches and unauthorized access still occur.
Users must be mindful of app permissions, storage practices, and terms of service before syncing their health information to cloud platforms. Governments and regulatory bodies are now enforcing stricter guidelines to ensure user data protection, but it remains the user’s responsibility to choose reputable brands and secure networks.
Not a Replacement for Medical Care
It’s important to note that while smartwatches are impressive tools, they are not replacements for professional medical equipment or consultations. These devices provide helpful insights but lack the precision and clinical oversight of formal healthcare settings.
Doctors in 2025 caution users to treat smartwatches as complementary tools—excellent for spotting trends and encouraging healthier behavior—but not suitable for self-diagnosing complex conditions. Overreliance on smartwatch data, without professional guidance, can result in missed diagnoses or improper self-treatment.
Conclusion
Smartwatches have redefined how people approach personal health, offering unprecedented access to real-time data, personalized insights, and motivation. In 2025, their integration into healthcare routines and everyday life reflects a broader shift toward proactive, tech-supported wellness. However, these devices are not without challenges—from accuracy limitations and battery demands to privacy risks and mental health implications.
Ultimately, the benefits of using a smartwatch for health monitoring outweigh the drawbacks when the device is used responsibly. By combining wearable technology with professional healthcare guidance and a balanced mindset, users can harness the full potential of smartwatches to lead healthier, more informed lives.